The development of Artificial Intelligence has been one of the most impactful innovations in the past couple of years. It has and will continue to have significant transformational impact on technology as well as humans. With massive amount of data, AI enables machine to become smarter and more intelligent over time and perform tasks on their own with little or without intervention.
AI for Cyber Security
Analyzing and responding to cyber threat is not human scalable problem. Applying AI to Security tools and techniques are critical in helping to detect and respond to security issues faster, saving costs and greatly reducing risk. Machines can learn based on past behavior to identify new attacks, distinguish malicious signals from benign signals, and can trigger workflows or recommend remediation actions.
Why Cyber Security needs AI?
The need for leveraging AI in Cybersecurity is especially crucial due to several converging trends.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, cyberattacks are the fastest growing crime in the U.S., and they are increasing in size, sophistication and cost. Cybercrime will cost the
world $6 trillion annually by 2021, up from $3 trillion in 2015 and is projected to cost the world $10.5 Trillion annually by 2025.
At the same time, CSO Online reports that there is a global cybersecurity skills shortage and states that research data clearly indicates that this situation not only isn’t improving, but it may in fact be getting worse. The primary ramifications of the skills shortage include an increasing workload on the existing cybersecurity staff, long-standing open jobs, an increase in hiring and training junior personnel, and an inability to learn or utilize security technologies to their full potential. Only 7% of
cybersecurity professionals claim that their organization has improved its position relative to the cybersecurity skills shortage over the past few years. Alternatively, 45% say that things have gotten worse while 48% believe things are about the same today as they were in the past.
And lastly, hackers are now deploying AI and machine learning in their attack strategies, all the more reason that AI must be applied in every organization’s security
strategy.
AI Basics
Artificial Intelligence is intelligence demonstrated by machine which mimics “cognitive” function that human associates with human mind. Machine Learning, Expert System, Deep learning are all subsets today’s AI technology.
- Expert system: It emulates decision making ability of human expert to generate
reasons or recommendations for solving certain problems. It usually comprises a
set of pre-configured rules.
- Machine learning: The system generates insights/patterns from large amount of data. If it comes from labeled data, it is called supervised learning; Otherwise it is called supervised learning.
- Deep learning: deep learning is modern “scalable machine learning” which does not require humans to conduct feature extraction, which is an important step in traditional machine learning.
AI in Cyber Security
AI can be utilized in multiple aspects of cybersecurity from detection to analysis, to remediation and response. Some common use cases include:
- Sifting through the myriad of alerts and identifying true from false positives at a certain level of accuracy
- Discovering patterns across signals automatically
- Based on the context, provide actionable recommendations
- Learning from past behavior to recommend relevant insights or suggestions to provide new context
- Essentially, AI can help to resolve and remediate any security issue faster and more effectively.
Too many alerts and too little resources?
How is AI Different from Automation?
Automation is simply automating low level, repetitive tasks using machines. AI involves intelligence and learning capabilities, distills new insights and becomes smarter over time.
How is AI Different from Data Analytics?
To put things simply, the difference between AI and Data Analytics is that Data Analytics is a traditional analysis to enable drawing conclusions and generating insights from large static data sets; it is not evolving or self-learning. AI has a learning capability that provides insights and becomes smarter over time.
AI: Hype vs Reality
Given the hyper of AI, it almost becomes a buzz in many areas. It makes people believe that AI can solve cyber security issues over night. This is wrong. AI is not magic and there is no silver bullet on solving cyber security problems. AI’s value to cyber security is to augment security analysts with powerful tools to better handle security issues, to simplify knowledge transfer and to free up resources for more important tasks.
Most of AI algorithms are known be a black box and the results are hard to interpret. That is one of the reasons why many people are skeptical of AI.
DTonomy’s Takes and Difference
Keeping AI as black box will just confuse security analysts and discourage technology adoptions. When designing AI system, we follow these design principles:
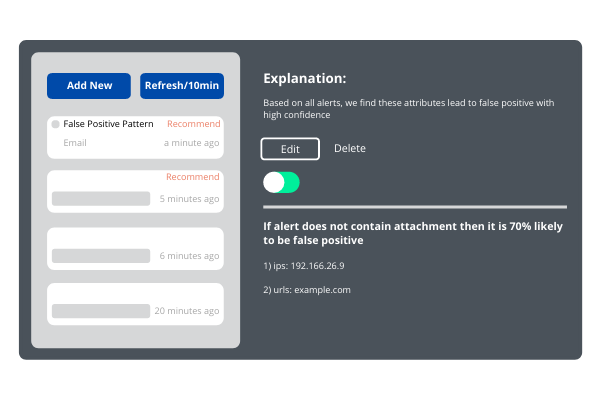
- Explainable
AI should provide deep yet clear insights that can be understood and explainable to humans, no matter how non trivial it may be. And, insights should always be supported by data and evidence
- Controllable
Analysts should have the flexibility to edit what AI suggests in an intuitive way. AI is under the security analysts’ control; however, the analyst does not need to master the complicated part of an AI model that professional data scientists work on. A security analyst should be able to control AI in an easy and intuitive way.
- Adaptive
An AI engine must continuously compute and listen to the security analyst’s feedback and be able to provide refreshed insights about a unique environment and new data sets.

